Cosmetic Standards and Regulations in Force in Europe

In publication #002 of Edukation we deal in depth with cosmetic regulations in Europe. We start with the current cosmetic standards followed by their definition, annexes and labeling. We continue with a user case from Spain. Finally, we end with the sections on responsible person, notification portal and claims.
Cosmetic Standards and Regulations in Force in Europe
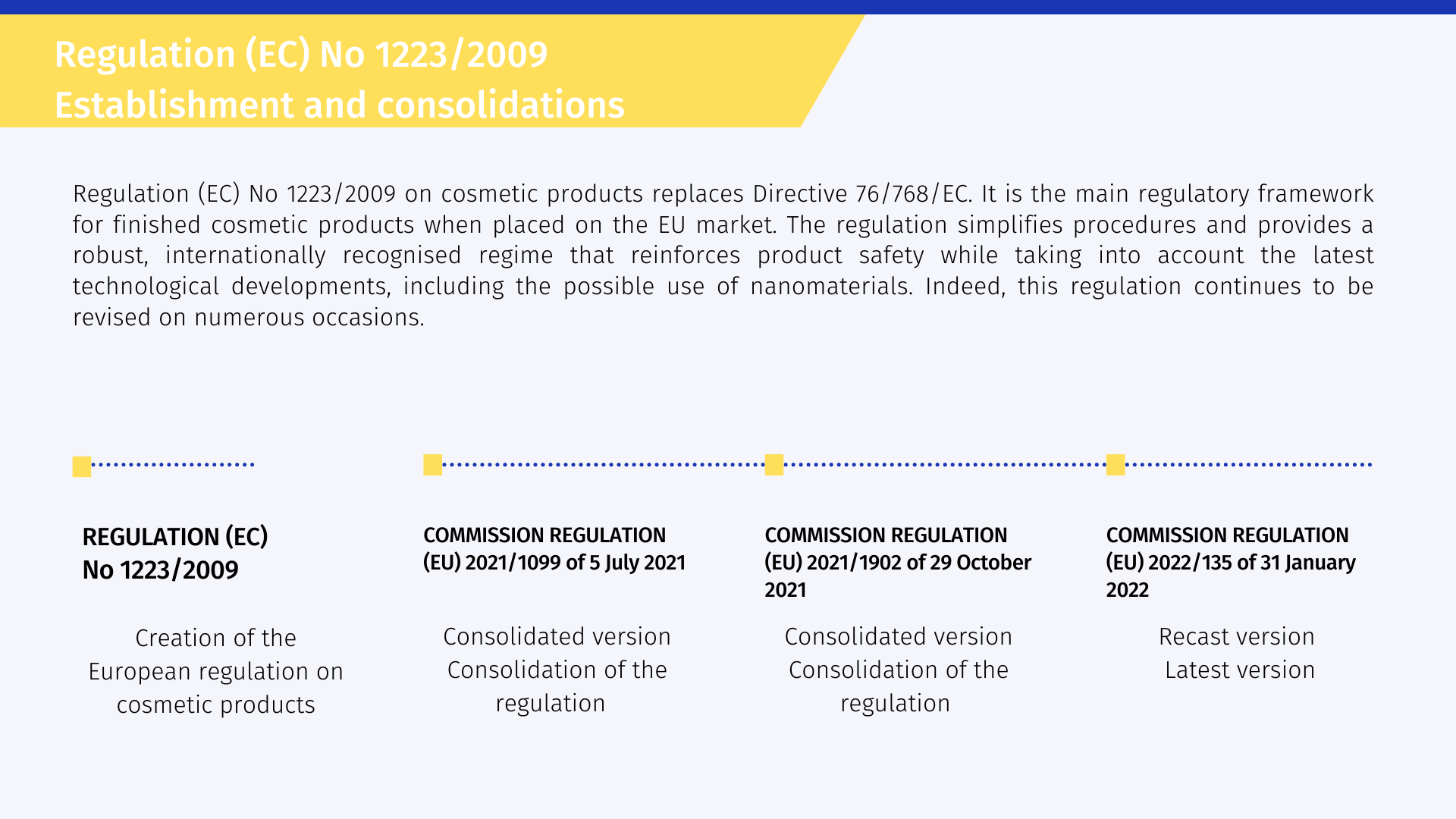
Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 [1] on cosmetic products is the main regulatory framework for finished cosmetic products when placed on the EU market. It reinforces the safety of cosmetic products and streamlines the framework for all operators in the sector. The regulation simplifies procedures and provides a robust, internationally recognized regime that reinforces product safety while taking into account the latest technological developments, including the potential use of nanomaterials. This regulation brings important new elements in comparison with the previous directive:
- Strengthening of the safety requirements for cosmetic products: Manufacturers must follow specific requirements in drawing up a product safety report before placing a product on the market.
- Introduction of the concept of responsible person: only cosmetic products for which a natural or legal person in the EU is designated as responsible person may be placed on the market.
- Centralized notification of all cosmetic products placed on the EU Market: Manufacturers will have to notify their products only once: via the EU Cosmetic Product Notification Portal (CPNP).
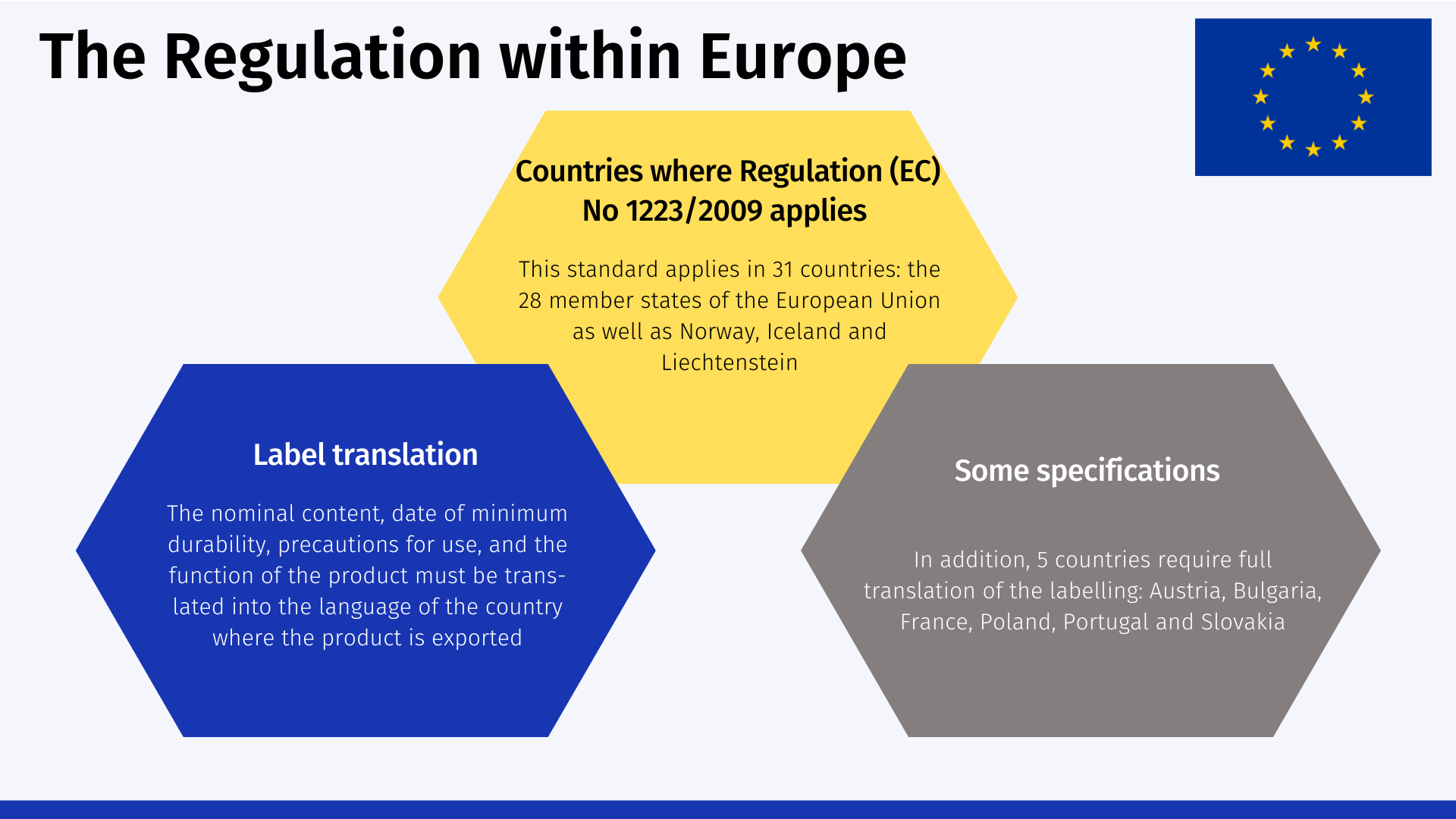
This standard applies in 31 countries: all 28 EU member states, as well as Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein.
Definition and Annexes
Regulation (EC) no 1223/2009 defines a cosmetic product and the annexes determine the lists of prohibited, restricted or permitted ingredients.
- Annex I: Determines the content of the cosmetic product safety report
- Annex II: List of substances prohibited in cosmetic products
- Annex III: List of substances which cosmetic products must not contain except subject to the restrictions laid down.
- Annex IV: List of colorants allowed in cosmetic products
- Annex V: List of preservatives allowed in cosmetic products
- Annex VI: List of UV filters allowed in cosmetic products

Substances classified as CMR are prohibited according to article 15 of the regulation. Proposals for classification as dangerous substances are submitted to echa, which determines whether or not to include them in the harmonized list of dangerous substances [2] (Annex 4, Table 3) (Last Update Annex VI CLP_ATP17 to be implemented on December 17, 2022 ). Products containing nanomaterials are also under close surveillance, a recommendation concerning their definition has been published (10 June 2022).
Labelling
Chapter VI deals with Consumer Information, and Article 19 focuses more precisely on the labelling of cosmetic products. In order to place a new product on the market, its label must contain the following information in indelible, easily legible and visible lettering.
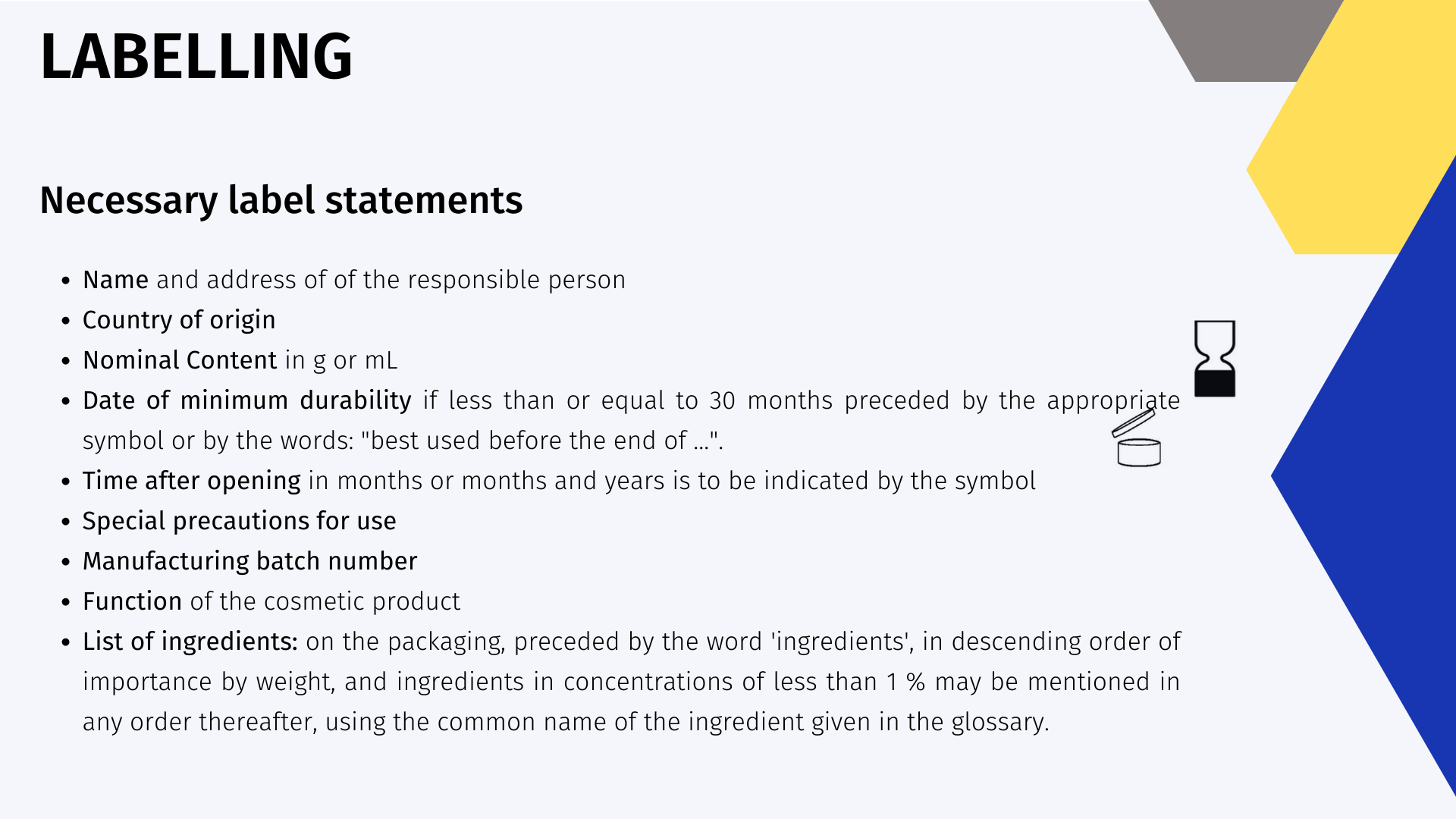
If the cosmetic product is too small to put all the information on a label, the information shall be indicated on an accompanying leaflet and shall be provided by an abbreviated indication or by a symbol which shall appear in the container or packaging.
Some of the terms on the labels can be defined as follows:
- Nominal Content: [3] The nominal content can be statistically uncontrolled, so that the containers must be filled with a higher content than the nominal content in order to ensure the contents of the container. The contents of the container can be statistically adjusted by means of the filling check in accordance with the European directive. The e symbol can be used in conjunction with the nominal content when following the statistical fill level check in accordance with the directive.
- Green Dot: [4] A scheme in which participating organizations coordinate the collection, sorting and recovery of used packaging placed on the market. This system is administered in accordance with national packaging laws to which packaging manufacturers, fillers, retailers and importers adhere. The participating national systems operate independently.
- Single-use plastics: [5] This directive makes it mandatory to specify on single-use products, which have plastic packaging or applicators or wet wipes containing plastic.
The nominal content, date of minimum durability, precautions for use, and the function of the product must be translated into the language of the country where the product is exported. In addition, 5 countries require full translation of the labeling: Austria, Bulgaria, France, Poland, Portugal and Slovakia. These requirements appear in the specific legislation of each EU country.
Spanish example
For example, in Spain the RD 85/2018 [6] regulates specifically:
- The receipt and transmission of notifications of serious undesirable effects and serious health risks. The notification by health professionals or consumers of serious undesirable effects caused by cosmetic products to the National Competent Authorities, and therefore establish the Spanish cosmetovigilace system, through which information on serious undesirable effects caused by cosmetic products is collected and evaluated.
- The powers of inspection and adoption of health protection measures that correspond to these authorities, as well as the procedures to be followed for this purpose.
- The procedures for compliance with the principle of administrative cooperation, both between national and European authorities, and the national alert network for cosmetic products.
- The language used in the labelling and information file of cosmetic products.
- The establishment of economic operators in the field of cosmetic products, establishing a regime for companies manufacturing and importing cosmetic products.

Responsible person
Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 Defines the Concept of Responsible Person. Only cosmetic products for which a natural or legal person is designated as responsible person in the community may be placed on the market. This person ensures compliance with the requirements laid down and safety for human health. The responsible person may be the manufacturer, the importer, the distributor or another designated person established in writing within the community. Responsible persons have several obligations.

Cosmetics Product Notification Portal
The Cosmetics Product Notification Portal (CPNP) [7] is a free online notification system set up for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products. Once a product has been notified on the CPNP, there is no need for any further notification at national level within the EU. Before the cosmetic product is placed on the market, the responsible person will have to notify his product to the Commission via the CPNP. The following information is required:
- Category of the cosmetic product and its name (s) allowing its specific identification.
- Name and address of the responsible person
- Country of origin, in case of import
- Member State where the cosmetic product is placed on the market
- Contact details of a natural person to be contacted in case of need
- Presence of substances in the form of nanomaterials
- Name and CAS number of substances classified as CMRs
- Framework formulation allowing rapid and appropriate medical treatment in case of difficulties.
The responsible person shall also notify the commission the label and a photograph of the packaging. The CPNP also contains a separate module (Article 16) for cosmetic products containing nano-materials. This notification must be made in addition to the notification under Article 13.
The CPNP makes this information available electronically to:
- Competent Authorities (for the purposes of market surveillance, market analysis, evaluation and consumer information).
- Poison centres or similar bodies established by EU countries (for the purpose of medical treatment)
- Medical centres for the treatment of medical health incidents due to the use of cosmetic products
The CPNP is accessible to:
- Competent authorities
- European Poison Centres
- Cosmetic product managers
- Distributors of cosmetic products

Claims
In the labelling, marketing and advertising of cosmetic products, product claims must be justified, according to the European cosmetic regulation article 20. The regulation establishes these criteria for product claims, indicating which claims may or may not be made and how they must be justified , Always in the interest of consumer protection, with useful, understandable and reliable information, informing the end user of the characteristics and qualities of the cosmetic product.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing process of cosmetic products must comply with the quality standards defined in the Une-en-not 22716-2007 [8] Standard to ensure that the products are safe.
Naturals
To guarantee that users receive the products as specified in the labeling that it is a natural and/ or organic product, there are several private certifications such as: Cosmos, Bioinspecta/ Biovidasana, Natrue. There is also the ISO 16128 [9] Standard to calculate the percentage of natural and/or organic ingredients in formulas.
References
- EUR-Lex site. Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products (recast) (Text with EEA relevance) available at https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02009R1223-20220301&qid=1656484738160 (July. 2022)
- EUR-Lex site.Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 (Text with EEA relevance) available at https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/ALL/?uri=celex:32008R1272 (July. 2022)
- EUR-Lex site. Council Directive 76/211/EEC of 20 January 1976 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the making-up by weight or by volume of certain prepackaged products available at https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A31976L0211 (July. 2022)
- Packaging Recovery Organisation Europe. The green dot. https://www.pro-e.org/the-green-dot-trademark (July. 2022)
- EUR-Lex site. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2020/2151 of 17 December 2020 laying down rules on harmonised marking specifications on single-use plastic products listed in Part D of the Annex to Directive (EU) 2019/904 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the reduction of the impact of certain plastic products on the environment (Text with EEA relevance) available at https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32020R2151 (July. 2022)
- Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado:Real Decreto 85/2018, de 23 de febrero, por el que se regulan los productos cosméticos available at https://boe.gob.es/buscar/doc.php?id=BOE-A-2018-2693 (July. 2022)
- Cosmetic Product Notification Portal. CPNP. https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/cpnp/faq/?event=faq.show (July. 2022)
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 22716:2007: Cosmetics — Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) — Guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practices availabale at https://www.iso.org/standard/36437.html#:~:text=ISO%2022716%3A2007%20gives%20guidelines,of%20protection%20of%20the%20environment (July. 2022)
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 16128-1:2016: Guidelines on technical definitions and criteria for natural and organic cosmetic ingredients and products availabale at https://www.iso.org/standard/62503.html#:~:text=ISO%2016128%2D1%3A2016%20provides,are%20defined%20with%20associated%20restrictions (July. 2022)